The most important lesson from 50 years of research in educational technology
I was asked some time ago: ‘What is the most important thing you have learned from your 50 years of research into learning technologies?’
I had to think carefully about this. Here are some of the many lessons I learned:
- the Gartner hype cycle is very accurate in predicting the path of a new technology for teaching,
- the continued dominance of the in-person formal lecture, despite all the research on its lack of efficiency in helping students learn compared to learning design incorporating technology, which can be simply put as instructors’ resistance to change
- the potential and dangers of AI for teaching and learning
- the importance of an instructor’s deep subject knowledge combined with imagination for the successful use of technology in teaching
- that students need to learn how to use a technology effectively for learning; it doesn’t just happen
- there is no one super-technology (not even, or especially, AI).
However, I think the most important lesson is this:
Video is greatly underused in higher education teaching
There are massive amounts of excellent videos available for teaching in higher education, but these are hugely under-exploited. Video can do things that cannot be done in a classroom. Video has unique teaching benefits (affordances).
So my colleague Michael O’Donoghue, of the University of Manchester in England, and I decided to make a set of seven videos that highlight the unique affordances of video for teaching in higher education, based on. These seven videos are now available (as open educational resources)
Demonstrating the advantages of video for teaching in higher education
Goal
The seven videos in this series aim to encourage instructors in higher education to make better use of video in their teaching. To see each video, click on the illustrations or video titles below.
The seven videos
Video 1:
- describes some general benefits of video for teaching;
- suggests why video is so extremely underused in teaching;
- points out that there is a great amount of video already available for free use covering almost any topic and level of student;
- and introduces the concept of educational affordances of video, what video can do that cannot easily be done in a classroom

2. The Affordances of Video (24m05s)
Video 2 presents examples of eight specific educational affordances of video, from humanities, chemistry, anatomy, mathematics, environmental sciences, biology and nursing, and introduces the faculty that made some of these examples who are interviewed later in this series.
Videos 3-6 are interviews with faculty who made some of the videos included in Video 2 in this series. In each interview, the interviewee is asked why and how they made their videos, how students responded to the video, and their general views on using video for teaching.
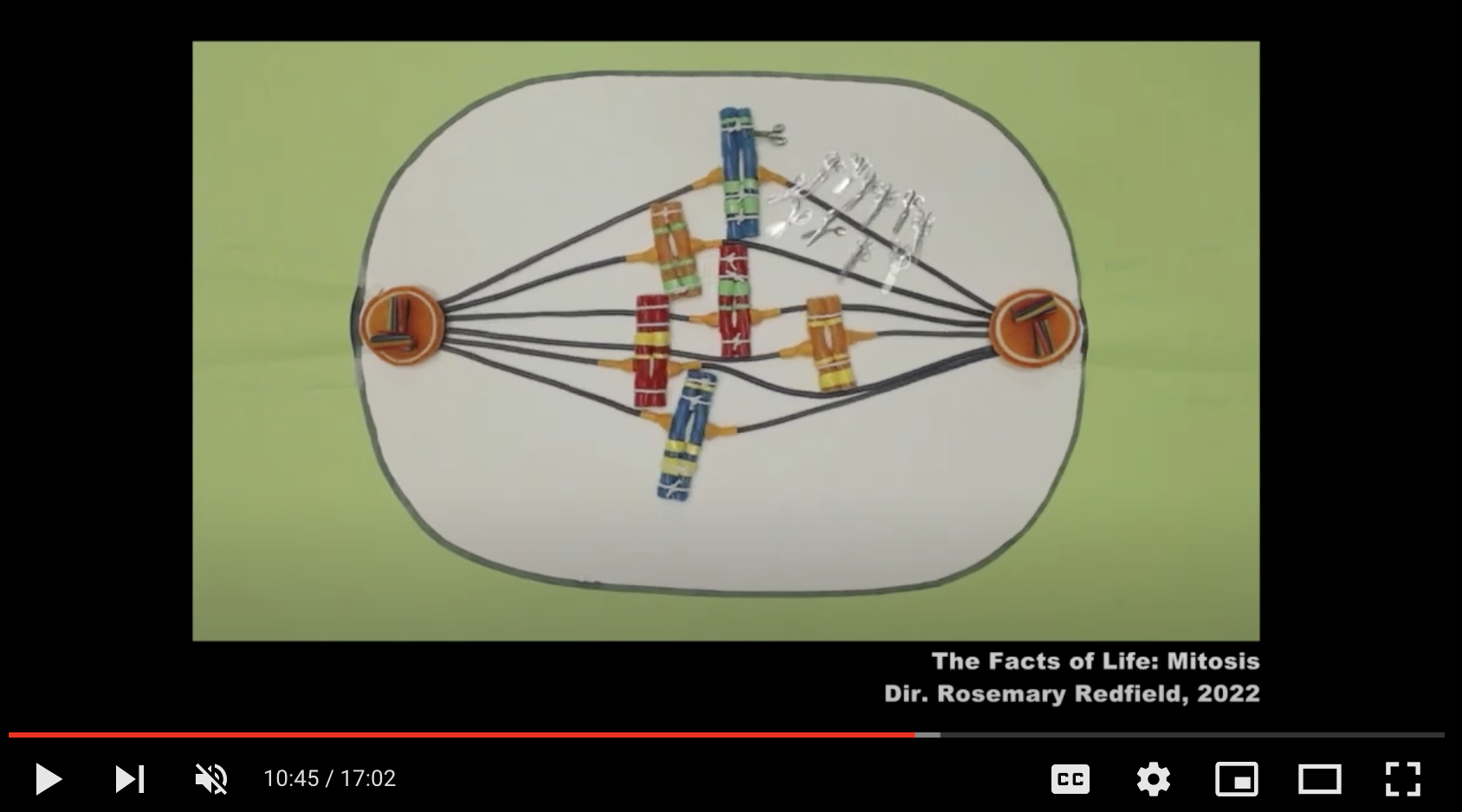
Video 3 is an interview with Professor Rosalind Redfield, Professor of Zoology at the University of British Columbia, who used stop animation with candy to explain a biological process that students rarely understand fully.
3. Animation: Video in the Life Sciences (17m02s)
Video 4 is an interview with Margaret Verkyl and Paula Mastrilli, at Centennial College and George Brown College, Toronto, who developed an interactive video game for nursing students on how to manage a difficult home visit
4. Interactive Games: Video in Health Assessment (12m45s)

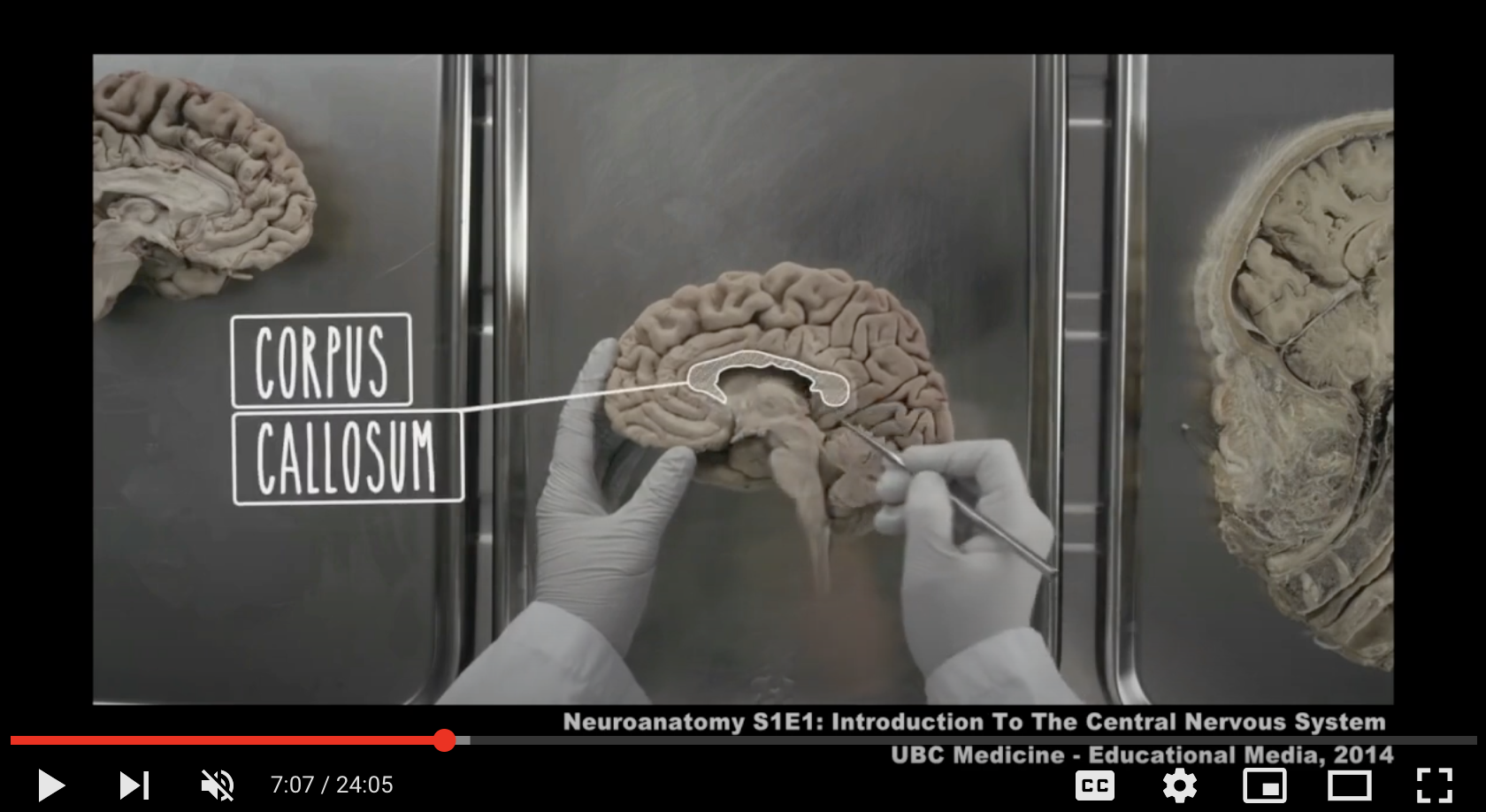
Video 5 is an interview with Professor Claudia Krebs, Professor of Anatomy at the University of British Columbia, who made a video on the anatomy of the brain, using an actual human brain
5. Video in Medical Education (8m32s)

Video 6 is an interview with Professor John Mason of the UK Open University, a pioneer in the use of video for teaching, where he explains (a+b)3 using a studio model of a cube
6. Video in Mathematics Education (20m27s)

Video 7 is a short video made by UBC Media Services demonstrating various studio arrangements available for use by faculty at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
7. Innovative and Accessible Video Production Services:

General benefits of video
Across the seven videos, the following general benefits of video are identified:
- Video can help learning in ways that are difficult to do in an in-person classroom (Video 1 generally, and all other videos in this series for specific examples)
- There is a wide range of already produced video material available online for free use: Video 1
- Thinking through the use of video can help even the instructor as well as the students to gain a deeper understanding of core concepts or processes: Video 3.
- Video can help even the most able students improve their learning outcomes: Video 4.
- Learning is a dynamic process and video can help students to develop a personal narrative about what they are learning that leads to deeper comprehension: Video 6
General barriers to greater use of video for teaching and learning
Video 1 identifies the following:
- Many instructors think incorporating video into their teaching is extra work
- Many don’t feel qualified to make or use video
- Many instructors are unsure what to use video for.
Affordances of video
There are many different ways that video can be used to provide distinct learning advantages over in-person classroom activities. The videos provide examples of 15 such affordances:
- Video is good for demonstrating examples of dynamic change: Videos 1, 2 and 3.
2. Video is good for providing concrete examples of abstract principles through the use of graphics and animation: Videos 1, 2 and 6.
3. Video is good for interpreting or analysing performance: Video 2.
4. Video can bring to students demonstration of activities and analysis by specialists in their field that may otherwise be difficult or impossible to provide because of location, timing, or being too dangerous for students: Video 2.
5. Video can or record and provide access to resources that are scarce or of limited availability: Video 2.
6. Video can be used to show the synthesis of a wide range of variables to suggest how real-world problems can be resolved, and to motivate students to action: Video 2.
7. Audio can offer the analysis or abstractions while the video image can give concrete images to support the analysis: Video 2.
8. Video can carry a strong affective or emotional impact for learners: Video 2.
9. Video can take a complex argument and compress it into a short time. (This allows or often requires follow-up discussion with the class – see requirements for success below): Video 2.
10. Video is good at demonstrating change over time through the use of animation, slow-motion, or speeded-up video: Video 2.
11. Video can be used to demonstrate decision-making processes or decisions in-action, by recording staged simulations, dramatisation, or role-playing: Videos 2 and 4.
12. Video can be used to provide opportunities for student decision-making and feedback on their decisions: Video 2.
13. Video is good for explaining complex processes difficult or impossible to observe with the human eye: Video 3.
14. Video-based games can elicit a strong emotional response from students, increasing their motivation and engagement: Video 4.
15. Video can be used where resources are scarce, or unsuitable for student experimentation, such as with live animals and human body parts: Video 5.
There are many more educational affordances being identified all the time across all subject disciplines.
Requirements for learning effectiveness
Just asking students to watch a video is usually insufficient for ensuring that learning will take place. Videos need to be embedded into a specific learning environment. This usually means providing guidance before viewing (why do they need to see it, and how will they benefit?) and follow-up work afterwards, such as questions about the video or other learning activities related to the video.
The videos also include other guidelines for success in using video effectively for learning:
Video 3: It’s important to identify key concepts or processes that students struggle with and think of ways in which video could help.
Video 3: It’s important to have a second set of eyes during the design and production of the video, whether it’s from a media producer or another educator, or even selected students.
Video 4: It is important that students are asked to engage with the video in preparation or in follow-up.
Video 5: It is important to find ways in which video:
- can explain concepts
- demonstrate processes
- provide student activities
that are difficult or not possible in a classroom.
Video 4: Making a viable video requires many iterations of a script and testing to ensure that students will understand and engage with the video.
Video 4: In many instances there are opportunities for funding some of the costs of developing videos, either through internal or external funding.
Video 5: It is really important to have a script that is both clear and succinct. This requires working in conjunction with students to ensure that they will fully understand what the video is showing.
Video 5: Although it is often possible to make excellent videos using very simple techno logy such as mobile phones, there will be circumstances where high quality production facilities will be needed.
Video 6: Professional production facilities can enable high-level representation or presentation of concepts that would be difficult or impossible to do in other ways.
Video for teaching in a digital age
These seven videos focus mainly on using professional or semi-professional production facilities. Today of course, many people make videos for social media using just a smartphone, and there is no reason why these should not be used for making and distributing educational videos. Indeed, we used a smartphone as a second camera for some of the interviews in this series. You can find more on producing quality video with a smartphone here:
[reference to come]
However, to produce quality video this way can be quite demanding on the instructor unless you can get additional help from your students. If your university and college has a media services unit, we would strongly advise you to seek their help, even if you wish to use just a smartphone.
Also these videos touch just the tip of the iceberg regarding using video for teaching. More can be found in Chapter 8.4 of Teaching in a Digital Age.
A list of participants in the videos
Presenter and content expert: Dr. Tony Bates: President and CEO of Tony Bates Associates Ltd, a private company specialising in consultancy and training in the planning and management of e-learning and distance education. Formerly Director of Distance Education and Technology at the University of British Columbia, Research Associate, Contact North Ontario, and Professor of Educational Media Research at the U,K. Open University.
Producer and Director: Michael O’Donoghue: Lecturer in Education at the Manchester Institute of Education (MIE), University of Manchester, UK with a focus on the use of educational video for supporting the UN Sustainable Development Goal 4, Quality Education.
Interviewees
Video 3: Professor Rosie Redfield, Professor of Zoology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Video 4: Margaret Verkyl, Professor of Nursing, Centennial College, Canada and Paula Mastrilli, Project Co-ordinator, George Brown College, Toronto, Canada
Video 5: Claudia Krebs, Professor of Anatomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Video 6: John Mason, Professor of Mathematics, Open University, Milton Keynes, U.K.
Your comments
We will be very pleased to hear from you if you have any comments, suggestions for improvement, or criticisms of the seven videos. Please use the comment box at the very end of this blog page.









 Dr. Tony Bates is the author of eleven books in the field of online learning and distance education. He has provided consulting services specializing in training in the planning and management of online learning and distance education, working with over 40 organizations in 25 countries. Tony is a Research Associate with Contact North | Contact Nord, Ontario’s Distance Education & Training Network.
Dr. Tony Bates is the author of eleven books in the field of online learning and distance education. He has provided consulting services specializing in training in the planning and management of online learning and distance education, working with over 40 organizations in 25 countries. Tony is a Research Associate with Contact North | Contact Nord, Ontario’s Distance Education & Training Network.


My graduate education courses were heavy with text. I tried to identify for each week a short video of 1 of the authors I invited students to read. It was nice to reduce the distance of the classics by showing short videos of some of the authors such as Michael Apple, A W (Tony) Bates, Isaiah Berlin, David Boud, Ernest Boyer, John Creswell, Guy Peters, William Pinar, Sheila Slaughter, Daniel L Stufflebeam, Etienne Wenger.
Completely agree, Gavin. Especially for online or distance courses, students report that seeing the instructor on video (or listening to them on a podcsast) makes the instructor feel more human or closer to the students.
Would any other instructors who have used video in their teaching like to comment on the benefits? (Or disadvantages)
This is all very useful advice and guidance for teachers but it is silent on how learners can get the most benefit from a video. The overriding tendency when watching a video is to be entertained due to the way that most are designed/devised and consumed which can lead to superficial or surface learning. Learners need to be given prompts and guidance on how to engage more deeply with them, including watching the video more than once if need be. Thus the contextual text and/or verbal instructions and activities that accompany the video can add a lot to a video’s impact.
I think it would be great if, alongside the instructional video, an activity is provided so that the learner can practice what they’ve learned. What we did in our company was to give the sales team a task. After learning the sales techniques, they had to purchase a product from the steel factory and then attempt to sell it to another learner. This way, they could practice the sales techniques with each other.
Excellent suggestion, Iran. I will think about this and probably using the accompanying web site, will add a list of possible activities for each video. Readers of this blog are welcome to make suggestions for this! What activities would you suggest?